U.S. Current Time & Time Zone Map & Time Zone
Live time zones for all U.S. states and territories
Alaska
Standard Time
AKST(UTC-9)
Aleutian
Standard Time
HAST(UTC-10)
Samoa
Standard Time
SST(UTC-11)
Pacific
Mountain
Standard Time
MST(UTC-7)
Central
Standard Time
CST(UTC-6)
Eastern
Standard Time
EST(UTC-5)
Arizona Mountain
Standard Time
MST(UTC-7)
Hawaii
Standard Time
HST(UTC-10)

Chamorro
Standard Time
CHST(UTC+10)
Atlantic
Standard Time
Puerto Rico / US Virgin Islands
AST(UTC-4)
1. How Many Time Zones Does the United States Have?
The United States and its territories legally recognize 9 time zones. However, when including the time zones of Howland Island and Baker Island—two uninhabited U.S. territories—the total reaches 11 time zones.
The continental United States has 4 standard time zones. Additionally, Alaska, Hawaii, and 5 U.S. territories each have their own time zones. Since Hawaii and these 5 territories do not observe Daylight Saving Time (DST), there are only 6 corresponding DST time zones.
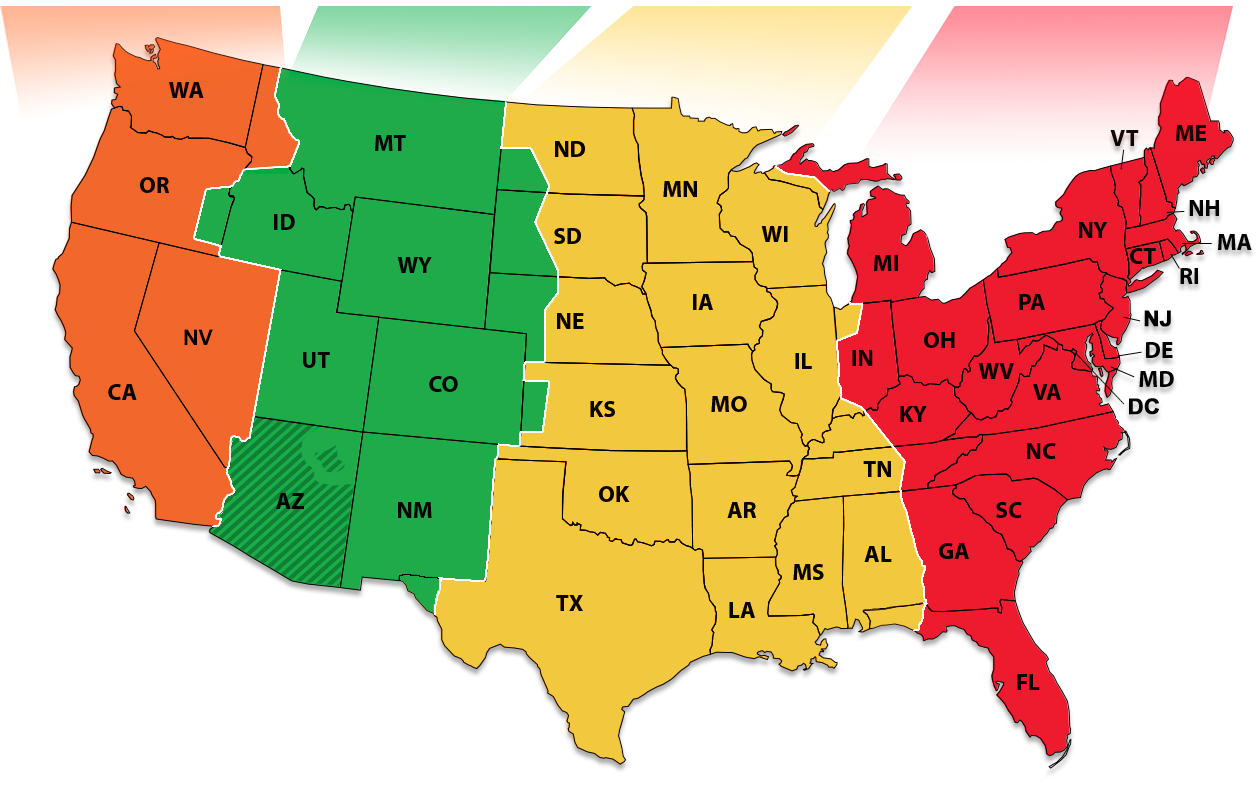
2. U.S. Time Zones by State & Territory (Map Reference)
Aleutian Standard Time (HADT/HST)
Parts of Alaska
HADT (Hawaii-Aleutian Daylight Time) is UTC-9 when daylight saving time is in effect; HST (Hawaii-Aleutian Standard Time) is UTC-10 during standard time.
Samoa Standard Time (SST)
American Samoa
SST (Samoa Standard Time) is UTC-11 and does not observe daylight saving time. This time zone remains constant throughout the year.
Pacific Standard Time (PST/PDT)
Washington (WA), Oregon (OR), Nevada (NV), California (CA)
PST (Pacific Standard Time) is UTC-8 during standard time; PDT (Pacific Daylight Time) is UTC-7 when daylight saving time is observed.
Arizona Mountain Standard Time (MST)
Arizona (AZ)
MST (Mountain Standard Time) is UTC-7 and does not observe daylight saving time. Arizona remains on standard time year-round, except for the Navajo Nation which does observe DST.
Mountain Standard Time (MST/MDT)
Montana (MT), Idaho (ID), Wyoming (WY), Utah (UT), Colorado (CO), New Mexico (NM)
MST (Mountain Standard Time) is UTC-7 during standard time; MDT (Mountain Daylight Time) is UTC-6 when daylight saving time is observed.
Central Standard Time (CST/CDT)
North Dakota (ND), South Dakota (SD), Nebraska (NE), Kansas (KS), Oklahoma (OK), Texas (TX), Minnesota (MN), Iowa (IA), Missouri (MO), Arkansas (AR), Louisiana (LA), Wisconsin (WI), Illinois (IL), Tennessee (TN), Mississippi (MS), Alabama (AL)
CST (Central Standard Time) is UTC-6 during standard time; CDT (Central Daylight Time) is UTC-5 when daylight saving time is observed.
Eastern Standard Time (EST/EDT)
Michigan (MI), Indiana (IN), Ohio (OH), Kentucky (KY), West Virginia (WV), Virginia (VA), North Carolina (NC), South Carolina (SC), Georgia (GA), Florida (FL), Maine (ME), Vermont (VT), New Hampshire (NH), Massachusetts (MA), Rhode Island (RI), Connecticut (CT), New York (NY), Pennsylvania (PA), New Jersey (NJ), Delaware (DE), Maryland (MD), District of Columbia (DC)
EST (Eastern Standard Time) is UTC-5 during standard time; EDT (Eastern Daylight Time) is UTC-4 when daylight saving time is observed.
Hawaii Standard Time (HST)
Hawaii (HI)
HST (Hawaii Standard Time) is UTC-10 and does not observe daylight saving time. Hawaii remains on standard time year-round.
Chamorro Standard Time (CHST)
Guam
CHST (Chamorro Standard Time) is UTC+10 and does not observe daylight saving time. This time zone remains constant throughout the year.
Atlantic Standard Time (AST)
Puerto Rico (PR), United States Virgin Islands (USVI)
AST (Atlantic Standard Time) is UTC-4 and does not observe daylight saving time. These territories remain on standard time year-round.
3. Daylight Saving Time schedule (U.S.)
Begins on the second Sunday in March at 2:00 a.m. local time (clocks move forward to 3:00 a.m.).
Ends on the first Sunday in November at 2:00 a.m. local time (clocks move back to 1:00 a.m.).
DST is not observed in Hawaii, most of Arizona (except the Navajo Nation), and the U.S. territories of Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands, Guam, American Samoa, and the Northern Mariana Islands.
4. History of U.S. Time Zones
On November 18, 1883, the United States was divided into 4 standard time zones, with the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) responsible for governing these zones. Since 1967, the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) has been responsible for managing America's time zones.
U.S. time zones are defined in Title 15, Chapter 6, Subchapter IX of the U.S. Code, under "Standard Time." The time zones in the law are defined by their offset from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).
U.S. law recognizes 9 official time zones. Additionally, the uninhabited territories of Baker Island (AoE) and Wake Island (WAKT) atoll add to the time zone count, bringing the total number of U.S. time zones to 11.
Nearly all states in the United States observe Daylight Saving Time (DST). Arizona and most of Hawaii do not observe DST. Indiana introduced DST in 2006.
5. Learn More About U.S. Time Zones
For comprehensive information about time zones in the United States, including detailed historical background, legal definitions, and current regulations, visit the official Wikipedia page:
Time in the United States - Wikipedia (opens in new tab)
U.S. Current Time & Time Zone Map & Time Zone
Live time zones for all U.S. states and territories
Pacific
Standard Time
PST(UTC-8)
Mountain
Standard Time
MST(UTC-7)
Central
Standard Time
CST(UTC-6)
Eastern
Standard Time
EST(UTC-5)
Arizona Mountain
Standard Time
MST(UTC-7)

Alaska
Standard Time
AKST(UTC-9)
Hawaii
Standard Time
HST(UTC-10)
Aleutian
Standard Time
HAST(UTC-10)
Samoa
Standard Time
SST(UTC-11)
Chamorro
Standard Time
CHST(UTC+10)
Atlantic
Standard Time
AST(UTC-4)
1. How Many Time Zones Does the United States Have?
The United States and its territories legally recognize 9 time zones. However, when including the time zones of Howland Island and Baker Island—two uninhabited U.S. territories—the total reaches 11 time zones.
The continental United States has 4 standard time zones. Additionally, Alaska, Hawaii, and 5 U.S. territories each have their own time zones. Since Hawaii and these 5 territories do not observe Daylight Saving Time (DST), there are only 6 corresponding DST time zones.
2. U.S. Time Zones by State & Territory (Map Reference)
Aleutian Standard Time (HADT/HST)
Parts of Alaska
HADT (Hawaii-Aleutian Daylight Time) is UTC-9 when daylight saving time is in effect; HST (Hawaii-Aleutian Standard Time) is UTC-10 during standard time.
Samoa Standard Time (SST)
American Samoa
SST (Samoa Standard Time) is UTC-11 and does not observe daylight saving time. This time zone remains constant throughout the year.
Pacific Standard Time (PST/PDT)
Washington (WA), Oregon (OR), Nevada (NV), California (CA)
PST (Pacific Standard Time) is UTC-8 during standard time; PDT (Pacific Daylight Time) is UTC-7 when daylight saving time is observed.
Arizona Mountain Standard Time (MST)
Arizona (AZ)
MST (Mountain Standard Time) is UTC-7 and does not observe daylight saving time. Arizona remains on standard time year-round, except for the Navajo Nation which does observe DST.
Mountain Standard Time (MST/MDT)
Montana (MT), Idaho (ID), Wyoming (WY), Utah (UT), Colorado (CO), New Mexico (NM)
MST (Mountain Standard Time) is UTC-7 during standard time; MDT (Mountain Daylight Time) is UTC-6 when daylight saving time is observed.
Central Standard Time (CST/CDT)
North Dakota (ND), South Dakota (SD), Nebraska (NE), Kansas (KS), Oklahoma (OK), Texas (TX), Minnesota (MN), Iowa (IA), Missouri (MO), Arkansas (AR), Louisiana (LA), Wisconsin (WI), Illinois (IL), Tennessee (TN), Mississippi (MS), Alabama (AL)
CST (Central Standard Time) is UTC-6 during standard time; CDT (Central Daylight Time) is UTC-5 when daylight saving time is observed.
Eastern Standard Time (EST/EDT)
Michigan (MI), Indiana (IN), Ohio (OH), Kentucky (KY), West Virginia (WV), Virginia (VA), North Carolina (NC), South Carolina (SC), Georgia (GA), Florida (FL), Maine (ME), Vermont (VT), New Hampshire (NH), Massachusetts (MA), Rhode Island (RI), Connecticut (CT), New York (NY), Pennsylvania (PA), New Jersey (NJ), Delaware (DE), Maryland (MD), District of Columbia (DC)
EST (Eastern Standard Time) is UTC-5 during standard time; EDT (Eastern Daylight Time) is UTC-4 when daylight saving time is observed.
Hawaii Standard Time (HST)
Hawaii (HI)
HST (Hawaii Standard Time) is UTC-10 and does not observe daylight saving time. Hawaii remains on standard time year-round.
Chamorro Standard Time (CHST)
Guam
CHST (Chamorro Standard Time) is UTC+10 and does not observe daylight saving time. This time zone remains constant throughout the year.
Atlantic Standard Time (AST)
Puerto Rico (PR), United States Virgin Islands (USVI)
AST (Atlantic Standard Time) is UTC-4 and does not observe daylight saving time. These territories remain on standard time year-round.
3. Daylight Saving Time schedule (U.S.)
Begins on the second Sunday in March at 2:00 a.m. local time (clocks move forward to 3:00 a.m.).
Ends on the first Sunday in November at 2:00 a.m. local time (clocks move back to 1:00 a.m.).
DST is not observed in Hawaii, most of Arizona (except the Navajo Nation), and the U.S. territories of Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands, Guam, American Samoa, and the Northern Mariana Islands.
4. History of U.S. Time Zones
On November 18, 1883, the United States was divided into 4 standard time zones, with the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) responsible for governing these zones. Since 1967, the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) has been responsible for managing America's time zones.
U.S. time zones are defined in Title 15, Chapter 6, Subchapter IX of the U.S. Code, under "Standard Time." The time zones in the law are defined by their offset from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).
U.S. law recognizes 9 official time zones. Additionally, the uninhabited territories of Baker Island (AoE) and Wake Island (WAKT) atoll add to the time zone count, bringing the total number of U.S. time zones to 11.
Nearly all states in the United States observe Daylight Saving Time (DST). Arizona and most of Hawaii do not observe DST. Indiana introduced DST in 2006.
5. Learn More About U.S. Time Zones
For comprehensive information about time zones in the United States, including detailed historical background, legal definitions, and current regulations, visit the official Wikipedia page:
Time in the United States - Wikipedia (opens in new tab)